Theis equation calculator units: cm=centimeter, ft=foot, gal=gallon (U.S.), hr=hour, km=kilometer, m=meter, min=minute, s=second.
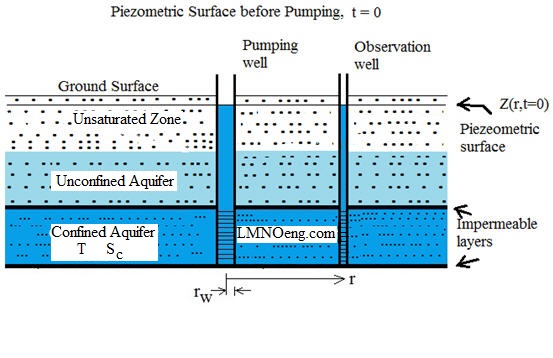
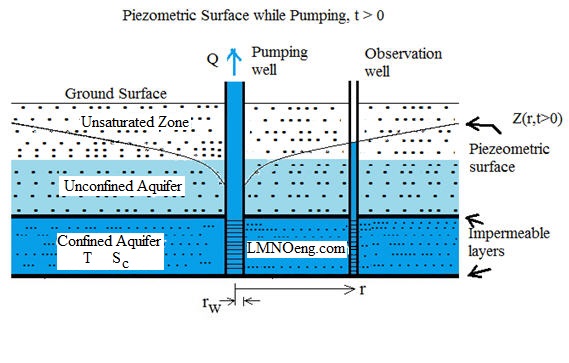
Diagrams of Groundwater Flow to a Pumping Well (Wells Screened in Confined Aquifer)
Theis Equation Calculator - Unsteady Groundwater Flow to a Pumping Well in a Confined Aquifer
Pumping water out of (or into) a confined aquifer is a common occurrence. The Theis equation calculator
computes the change in the piezometric surface as water is pumped. In a confined aquifer,
the piezometric surface is the elevation of the water surface in an observation well drilled into the
confined aquifer and screened in the confined aquifer. The water level rises above the upper confining layer.
Drawdown s is the difference between the
elevation of the piezometric surface prior to pumping Z(r,t=0) and the elevation
of the piezometric surface during pumping Z(r,t>0). Thus:
s(r,t) = Z(r,t=0) - Z(r,t>0).
Equation - Conservation of Mass
Unsteady groundwater flow to a pumping well in a confined aquifer is described by the equation (Bear, 1979, p. 320):
![]()
The equation describes mass conservation of groundwater flow in the radial direction allowing for change in storage volume (expansion or contraction of the confined water due to change in pressure).
Boundary Conditions
Pumping rate Q is positive but has a negative sign in the boundary condition equation below since water
goes toward the well when it is pumped. Water flowing toward the well is flowing in the
negative r direction. Thus, to define Q as positive when pumping water out of the aquifer,
the boundary condition needs a negative sign:
s(r=0,t=0) = 0 s(r=∞,t) = 0 ![]()
The goal of the Theis equation calculator is to solve for drawdown as a function of radial distance r from the pumping well at time t since pumping started. The solution is commonly called the Theis solution, after Charles Theis who developed the solution in 1935 (Bear, 1979, p. 321):
![]()
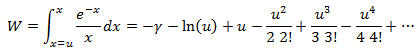
![]()
Our calculation carries out the series to the u100 term which is sufficient for convergence to machine precision for u up to 9.5.
Theis equation calculator for unsteady groundwater flow allows entry of either a positive or negative value for the pumping rate Q. A positive Q simulates pumping, and drawdown s will be positive since the piezometric surface drops. If a negative value is entered for Q, water injection is simulated. In that case drawdown is negative since the piezometric surface rises.
The groundwater flow calculator checks that r, t, T, and Sc are positive inputs. It also checks to make sure u ≤ 9.5 which is the maximum value printed in many texts (e.g. Bear, 1979, pp. 320-321). All input variables are converted to SI units prior to calculations.
The Theis equation calculator does not check if the input values are physically reasonable and does not check if Reynolds number Re is less than or equal to 1.0. Darcy's law for groundwater flow (expressed in the boundary condition above that has "-Q" in it) is only valid for Re ≤ 1. Darcy's law is typically valid in groundwater flow since water velocities are very low through porous subsurface formations.
Notation
Units shown in notation are SI. The groundwater calculation converts user-selected units to SI, performs calculations in SI,
then converts output variables to user-selected units.
Q = Steady pumping rate (m3/s).
r = Radial distance from centerline of pumping well (m).
rw = Pumping well radius (m).
s = Drawdown (m).
Sc = Confined aquifer storage coefficient.
t = Time since beginning of pumping (s).
T = Confined aquifer transmissivity (m2/s).
u = Collection of terms. Computed after all variables converted to SI units.
W = Theis well function.
Z = Elevation of piezometric surface (elevation that water rises to in observation well screened in confined aquifer) (m).
γ = Euler's constant = 0.5772156649... (Abramowitz & Stegun, 1972, p. 229).
π = Constant, 3.14159265...
ln( ) = Natural logarithm.
! = Factorial function.
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, I. A. 1972. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. Dover Publications, Inc.
Bear, J. 1979. Hydraulics of Groundwater. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
© 2017-2026 LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd. All rights reserved.
LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd.
7860 Angel Ridge Rd. Athens, Ohio 45701 USA Phone: (740) 707-2614
LMNO@LMNOeng.com
https://www.LMNOeng.com
