Units: abs=absolute, acfd=actual cfd, acfh=actual cfh,
acfm=actual cfm, cfd=cubic foot per day, cfh=cubic foot per hour, cfm=cubic foot per
minute, cfs=cubic foot per second, cm=centimeter, g=gram, hr=hour, kg=kilogram,
km=kilometer, kPa=kiloPascal, lb=pound, m=meter, mbar=millibar, mm=millimeter,
Mcfh=thousand cfh, MMcfd=million cfd, N/m2=Newton per square meter (same as
Pascal), psi=pound per square inch, psia=psi (absolute), psig=psi (gage), s=second,
scfd=std cfd, scfh=std cfh, scfm=std cfm, std=standard conditions.
Equations
In the gas flow discipline, flowrates are often expressed as "flow at standard
conditions". Standard conditions are synonymous with the term "base
conditions" or "normal conditions". The calculation on this page converts
between mass flow (W), flow at standard conditions (Qs), and flow at actual
(flowing) conditions (Qa). The equations use SI units, but our calculation
allows a variety of units with all of the unit conversions handled internally by the
program.
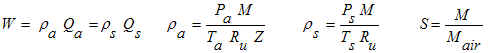
Standard (Base) Conditions
For the natural gas industry in North America and OPEC (Organization of Petroleum
Exporting Countries), standard conditions are typically Ps=14.73 psia and Ts=60oF.
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) uses Ts=0oC
and Ps=1 bar. Some gas flows related to environmental engineering are based on
standard conditions of Ts=15oC or 20oC and Ps=101.325
kPa (1 atmosphere). Standard conditions vary from industry to industry and have varied
over the years within the same field, so it is important to know the standard temperature
and pressure that a stated "standard flow" is based upon. Wikipedia (2006) has a
good discussion of standard conditions.
Notes about some confusions in the gas industry: In English units, the abbrevation "M" means thousand and "MM" means million. In metric units, "M" means mega which means million. You may see the notation "Nm3/s" which is a metric (SI) unit for "Normal m3/s". Normal is the same as standard or base, which can be confused with Newton (unit of force) since both have the same abbreviation. We don't use the unit "Nm3/s" on this page; instead, we call it "std m3/s".
Variables
The units refer to the units that must be used in the equations shown above. However, a
variety of units may be used in our calculation.
M = Molecular weight of the actual (flowing) gas (kg/mol). For example, methane (CH4)
has a molecular weight of 0.016042 kg/mol. Compute molecular
weight using our calculator.
Mair = Molecular weight of standard air = 0.02896443 kg/mol (CRC, 1983).
Pa = Absolute pressure at actual (flowing) conditions (N/m2
absolute).
Ps = Absolute pressure at standard (base) conditions (N/m2
absolute).
Qa = Flowrate at actual (flowing) conditions (m3/s).
Qs = Flowrate at standard (base) conditions (m3/s).
Ru = Universal gas constant = 8.3144126 N-m/mol-K (CRC, 1983, p. F-192).
S = Specific gravity of flowing gas (note that Sair=1). For example CH4
has S=MCH4/Mair= 0.016042 / 0.02896443 = 0.554
Ta = Absolute temperature at actual (flowing) conditions (K).
Ts = Absolute temperature at standard (base) conditions (K).
W = Mass flowate (kg/s).
Z = Gas compressibility factor which represents the gas's deviation from ideal gas
behavior. Typically 1.0 at standard conditions. Typically decreases as pressure
increases then increases at high pressure. Can be as low as 0.4 or so and up to 2 or
so. Exact computation depends on make-up of the gas, gas critical pressure and
temperature, and actual temperature and pressure. Additional information
can be found at Process (2003).
ρa = Greek letter rho. Density at actual (flowing) conditions,
kg/m3.
ρs = Greek letter rho. Density at standard (base) conditions,
kg/m3.
Error Messages
The following are error messages shown if input values are improper:
"Need Z > 0", "Need Pa , Ps > 0", "Need Ta , Ts > 0.0
K", "Need S > 0", "Need M > 0", "Need Qa > 0",
"Need Qs > 0", "Need W > 0".
References
Chemical Rubber Company (CRC). 1983. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Weast, Robert
C., editor. 63rd edition. CRC Press, Inc. Boca Raton, Florida. USA.
Process Associates of America. 2003. Gas compressibility factor (calculator uses Redlich Kwong equation). http://www.processassociates.com/process/property/z_factor.htm.
Wikipedia. 2006. Standard conditions for temperature and pressure. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_temperature_and_pressure.
© 2006-2026 LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd. All rights reserved.
LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd.
7860 Angel Ridge Rd. Athens, Ohio 45701 USA Phone: (740) 707‑2614
LMNO@LMNOeng.com
https://www.LMNOeng.com
