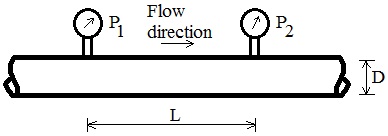
Pipe Pressure Drop Drawing and Equation:
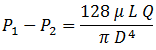
Discussion
Pressure drop in a pipe is an important concept in fluid dynamics and engineering, influencing the efficiency of fluid transport systems in various applications, from household plumbing to large-scale industrial processes. Pressure drop occurs when the pressure of a fluid decreases as it flows through a pipe. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon, such as friction losses, changes in pipe geometry, and the presence of fittings and valves. The calculator on this page determines pressure drop based on pipe friction for laminar flow in a horizontal pipe. We have other calculators that include additional factors leading to pressure drop.
The effects of pressure drop on a piping system can be substantial, impacting both the efficiency and the operation of the system. A significant pressure drop indicates that the piping system must work harder to pump the fluid (or require a higher elevation starting point) increasing the energy consumption of the pump. This inefficiency can lead to higher operational costs and reduced overall system performance.
The need for more powerful pumps to overcome pressure drops translates to higher energy costs. Further, the increased stress on these components can lead to more frequent maintenance or replacement, further driving up costs. Excessive pressure drops can lead to unstable flow conditions, which may cause vibrations and mechanical wear in the piping system. Over time, this can shorten the lifespan of the components and lead to frequent failures or downtime.
Addressing pressure drop in pipes involves several strategies aimed at reducing friction losses and optimizing system design. To reduce pressure drop, engineers can design pipes with smoother surfaces and larger diameters. Smooth surfaces reduce frictional resistance, while larger diameters lower the velocity for a given flow rate, thus reducing frictional losses.
Regular maintenance of the piping system to remove deposits, scale, and other obstructions can maintain optimal flow conditions and minimize pressure drop. Routine inspections and cleanings can prevent long-term issues related to pressure loss.
Equation Derivation
For steady flow of an incompressible fluid in a constant diameter horizontal pipe using the Darcy-Weisbach friction loss equation, the energy equation from location 1 to 2 is expressed in terms of pressure drop as:
![]()
where:
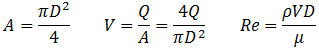
When Re < 2100, flow is laminar and:
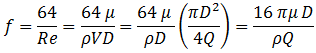
Then pressure drop is:
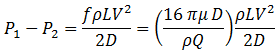
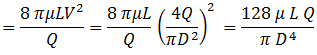
The final pressure drop equation is often called Poiseuille's law after the original researcher (Munson et al., 1998, p. 468).
Unit abbreviations, symbols: kg=kilogram, m=meter, N=Newton, s=second. A=Pipe area, f=Moody friction factor.
Reference for pressure drop: Munson, B. R. Young, D. F. and Okiishi, T. H. 1998.
Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. John Wiley and Sons. Inc. 3ed.
© 2017-2025 LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd. All rights reserved.
LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd.
7860 Angel Ridge Rd. Athens, Ohio 45701 USA Phone: (740) 707-2614
LMNO@LMNOeng.com https://www.LMNOeng.com
